Coronary Artery Segmentation using LadderNet
In the past years, many automatic segmentation strategies based on Deep Learning (LeCun, 2015) methodologies have been proposed for vessel segmentation. In this work we aim to train a LadderNet (Zhuang, 2019) network for coronary artery segmentation. Two different patch-to-patch training approaches (Sekoua, 2019) are compared.
Methods
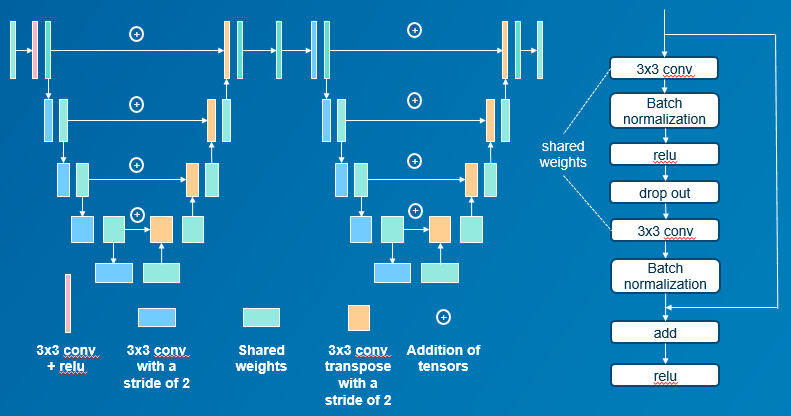
LadderNet was composed by two attached U-Nets (Ronneberger, 2015), with two encoder and two decoder branches in total. Two different datasets were used (Philips Healthcare, Best, The Netherlands), the first one as training dataset and the second for the evaluation. The training dataset was subdivided into two subdatasets. Subdataset1 consisted of 88 frames of size 1024x1024. For subdataset2, these frames were divided into patches of size 48x48 and 515 of them were selected, the proportion of patches with only background/vessel information was 80/20%. All images were segmented using ImageJ (NIH, USA).
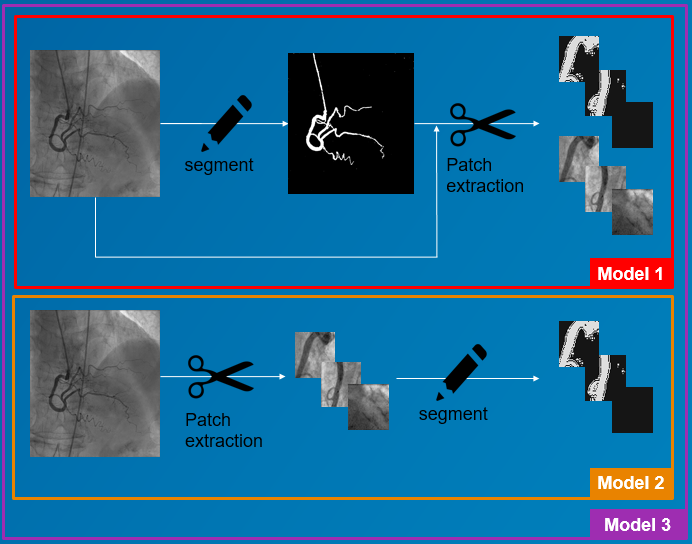
The first training strategy had three steps:
- Segmentation of subdataset1
- Patch extraction
- Network training
The second training method consisted in:
- Patch extraction
- Segmentation of subdataset2
- Using the weights from the first training strategy as starting point, the network was retrained with subdataset2
Results
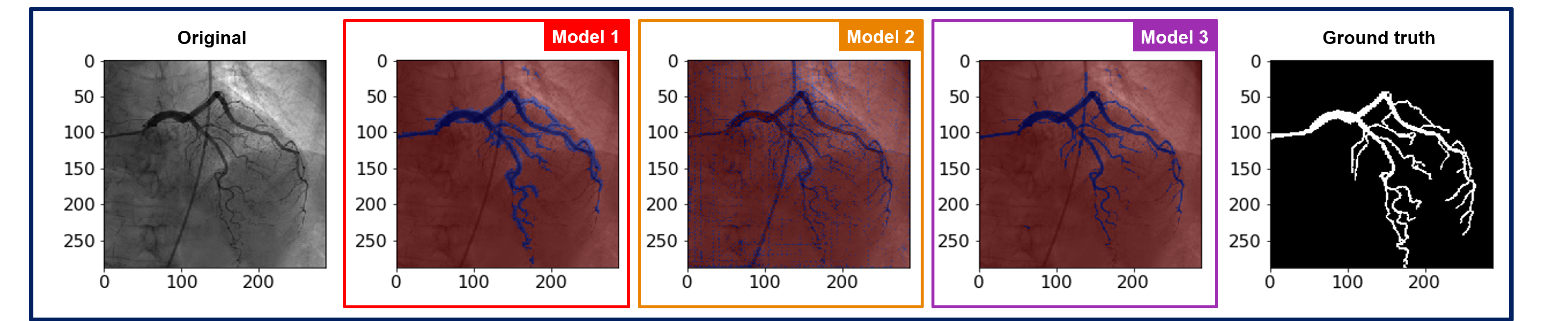
Figure 1 shows the results evaluated over the second dataset. The quality of the segmentation obtained with the second strategy is better, the delineation of the vessels is more accurate.
Discussion and conclusion
Some differences between the two results could be explained by differences in the two training subdatasets, as the presence of the catheter and a lower homogeneity within the big vessels in the second case.
Further work using training datasets with a higher number of patches and patches of different sizes is mandatory. Also, a quantitative evaluation of the results is required.
We can conclude the proposed LadderNet and the second training strategy used seem very promising to resolve coronary artery segmentation.
